Promote the satiety hormone GLP-1
GLP-1 is currently regarded as the weight loss miracle and is on everyone's lips. But what exactly is behind this hormone - and how can the body's own GLP-1 production be stimulated naturally?
GLP-1: satiety booster and insulin booster
GLP-1, or glucagon-like peptide 1, is a hormone that is produced in our intestines. It plays an important role in sugar metabolism, but also in the regulation of appetite: On the one hand, GLP-1 promotes the glucose-dependent release of insulin and lowers the production of glucagon, which promotes the release of glucose in the liver. On the other hand, it delays gastric emptying and promotes satiety by binding to receptors in the brain.

Influencing GLP-1 through diet
- Diet rich in fibre:
Fibre from wholegrain cereals, oatmeal or psyllium husks promotes GLP-1 secretion. Wholemeal products and oatmeal also contain complex carbohydrates and cause blood sugar levels to rise more slowly than white flour products - Protein-rich meals:
Proteins from whey, eggs or fish strongly stimulate GLP-1 release. The amino acid leucine is particularly important here.</li - Resistant starch:
When carbohydrates from potatoes, rice or pasta are cooled, the structure of the starch changes and resistant starch is formed, which the digestive enzymes can only break down to a limited extent. On the one hand, this increases GLP-1 production and also causes blood sugar levels to rise more slowly.</li

Exercise as a GLP-1 booster
The latest studies show a link between exercise and GLP-1 levels. Regular exercise not only supports the cardiovascular system, it also promotes GLP-1 levels and improves the microbiome. Of course, increased exercise, especially in conjunction with strength training, also leads to an increase in muscle mass. More muscle means more calories burned. But endurance training also increases the GLP-1 level. The current recommendation is 10,000 steps per day.

Plant substances as natural GLP-1 boosters
More and more plant substances are becoming the focus of GLP-1 research: berberine, a plant alkaloid that was first discovered in barberry, has been shown in studies to have a GPL-1-promoting effect. Curcumin, the main active ingredient in the spice and medicinal plant turmeric, also has a positive effect on GLP-1. Incidentally, we know turmeric as the colouring component of the curry spice. Another plant-based GLP-1 booster is resveratrol. Resveratrol is a plant substance that is mainly found in the skin of grapes, but also in dark chocolate and berries (raspberries, cranberries and redcurrants).

Medication with GLP-1 effect
Medicines such as Ozempic or Wegovy contain the active ingredient semaglutide. These drugs were developed to increase insulin production in type II diabetes patients. Semaglutide does not promote the body’s own GLP-1 production, it acts like GLP-1 itself by binding to the same receptor as GLP-1. Disadvantage: the rapid onset of action often leads to side effects such as persistent nausea, bloating and vomiting.
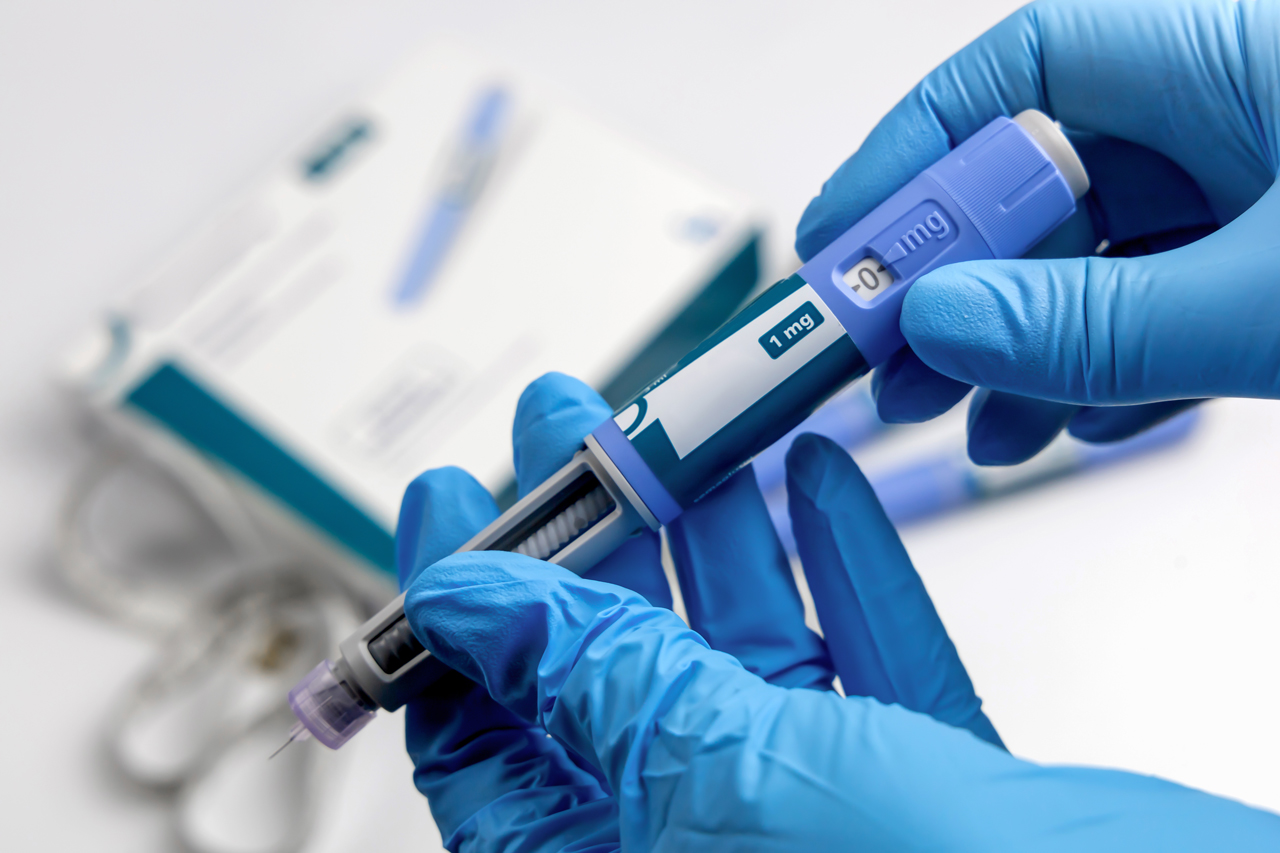
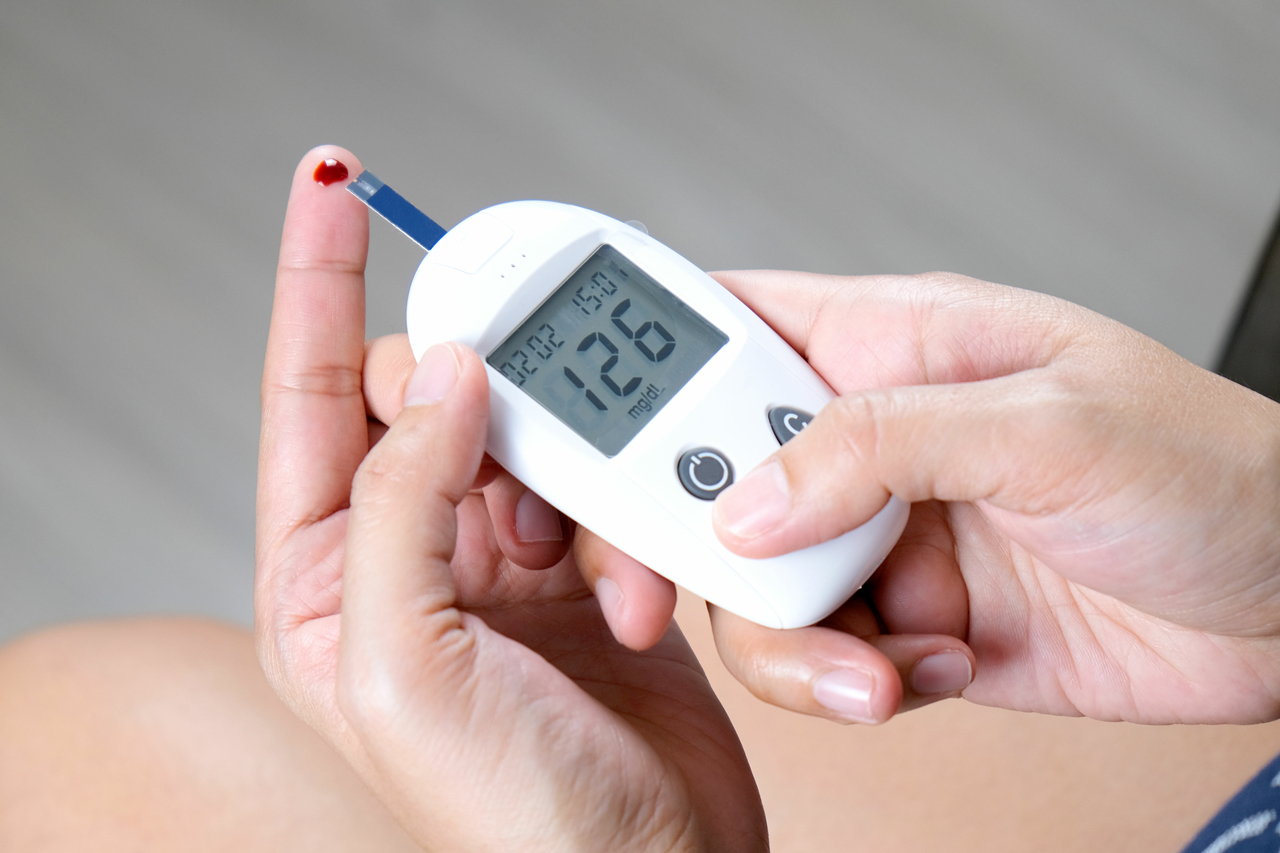
Avoidance of a rapid rise in blood sugar
Highly processed foods (ready-made products), foods and drinks with a high sugar content (soft drinks) and foods with a high white flour content cause blood sugar levels to rise very quickly and therefore have a counterproductive effect on GLP-1 formation. Sleep disorders with poor sleep quality and extreme stress also increase blood sugar levels.
A small detail in passing: if the blood sugar level rises very quickly, there is a rapid counter-regulation in the form of insulin. This causes the blood sugar level to drop rapidly and leads to food cravings. So here’s a little tip: a sweet snack immediately after the main meal causes the blood sugar level to rise less than if it is enjoyed in the afternoon without a meal beforehand.
Targeted health improvement through advanced micronutrient supplements: with our products, this is no utopia, but a tried and tested reality.













